
Date: 20 January 2025
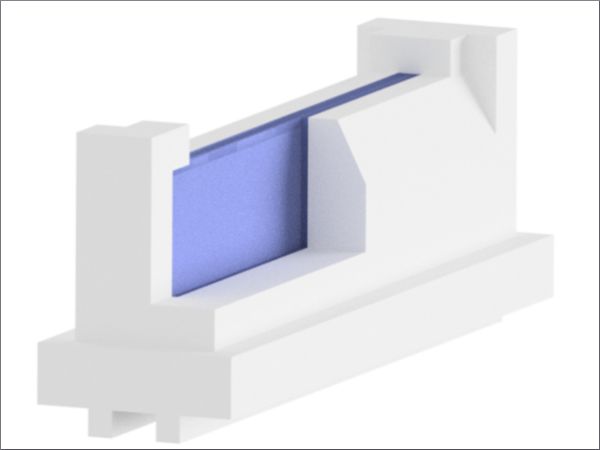
The molybdenum wall is used in basins of melting tanks in the area after the hot spot to separate the melting part from the refining part and thus prevent a short-circuit flow. It acts as a flow barrier, forcing the bottom glass to rise into the hot area of the hot spot, where it dissolves the last relics from the batch to refine bubbles in the glass. This ensures a better quality of the molten glass with a comparable energy input and/or a higher melting capacity with the same glass quality.
The molybdenum wall is installed in the basin of the furnace across the entire width of the basin between refractory bricks placed in front of and behind it. The molybdenum wall is anchored in the floor and stands stress-free between these bricks.
It consists of individual molybdenum plates that are held in molybdenum rods. The rods are anchored in the ground. The design takes into account the different thermal expansion of the various materials.
The Mo-Wall is characterised by the fact that its function remains unrestricted until the end of the furnace journey.
The wall is suitable for all standard glass types and all fossil-heated furnaces with and without boosting.
The exact dimensions are determined depending on the application.
During tempering and until the furnace is completely filled, the space between the AZS blocks is provided with a safety layer to prevent unwanted oxidation and sublimation of the molybdenum metal.
Features:
- Improved glass quality
- Greater flexibility
- Permanently secured function until the end of the furnace service life
- Simple design and installation
- Can be used in fossil-fuel heated furnaces, also with boosting
Technical data:
- Width of the wall: can be adapted to any width of the furnace
- Operating temperature: ... 1630 °C
- Glass types: Alkali - lime - glass, borosilicate glass, aluminosilicate glass, etc.
 600450
600450













Add new comment